Taiwan’s AMS BioteQ Develops a New Antimicrobial Dressing Which Accelerates Diabetes Wound Healing
Wound dressing can provide more than protection in chronic wound care. With the right material and antimicrobial properties, a dressing can bolster wound recovery and effectively supplement the treatment, especially for diabetes.
Challenges of Diabetes Wounds
Studies have shown patients with diabetes have a 10% rate of developing diabetic foot ulcers, and 25% of diabetic patients are admitted to hospital due to foot illnesses. Those patients have high blood sugar, which causes bad blood circulation, weakens white blood cells and increases the number of bacteria. Therefore, they have slow recovery rates and cannot generate enough immunity to combat infection. It’s also hard for treatments to get into the wound.
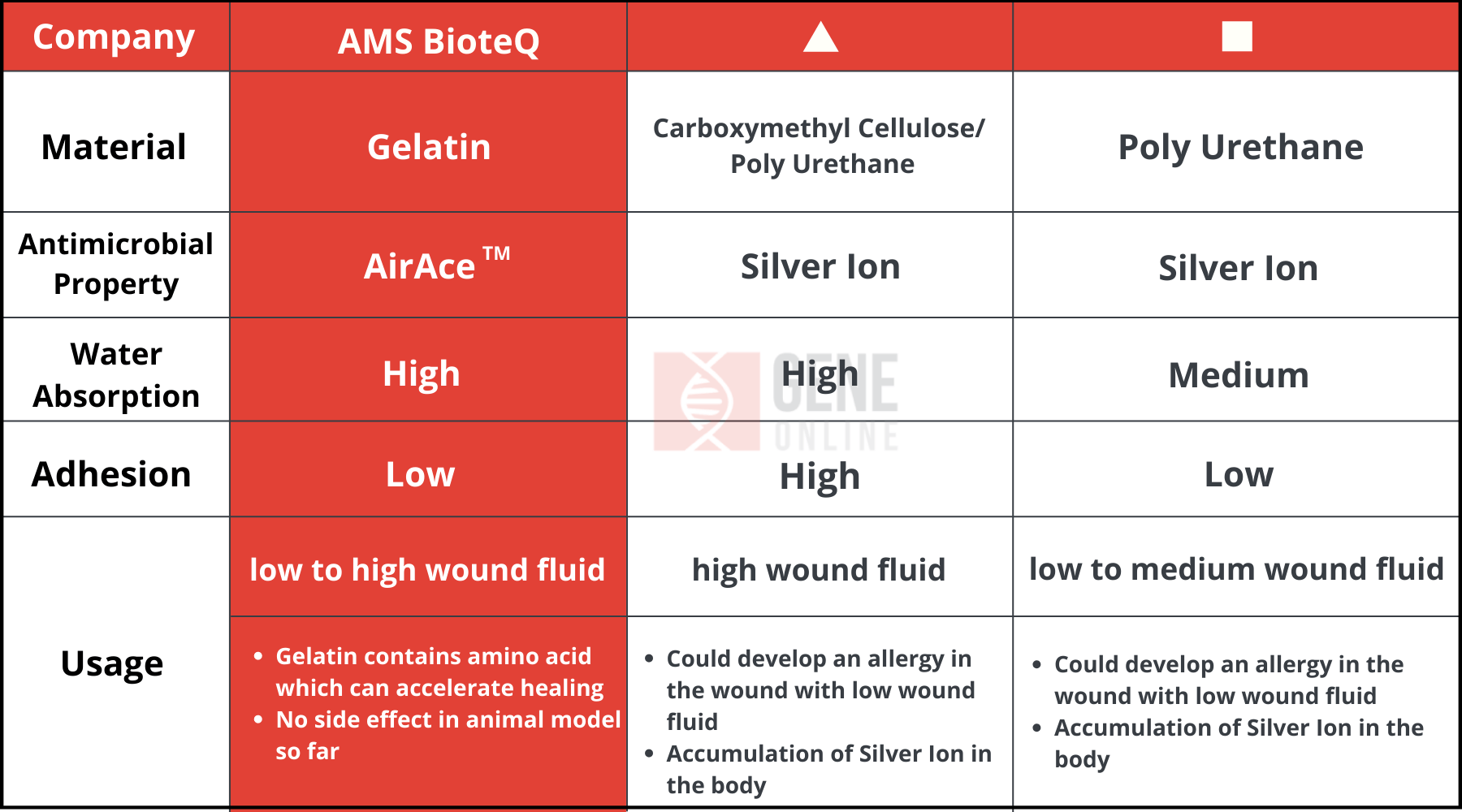
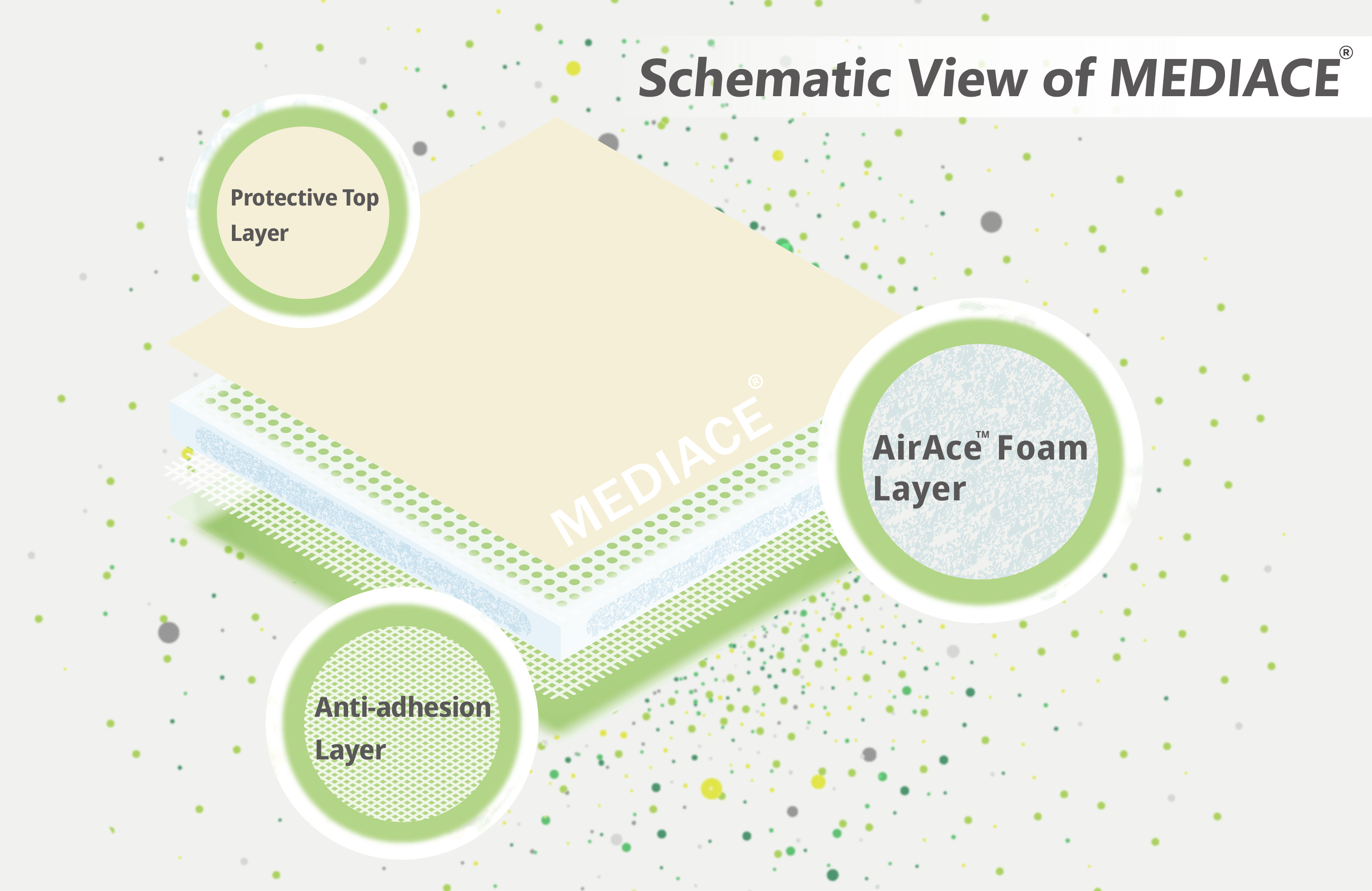
To accelerate the healing, Taiwan’s Anti-Microbial Savior BioteQ Co., Ltd. (AMS BioteQ) has developed a new antimicrobial dressing for chronic wounds. This dressing is called MEDIACE®. It utilizes the antimicrobial property AirAce™ extracted from medicinal fungi using the proprietary technology ExtrO™. The use of AirAce™ separates itself from other wound dressings on the market, which implement silver ions for the antimicrobial effect.
No Side Effects So Far in Animal Models
Dressings with silver ions take up most of the market, but trials have shown that these dressings can cause redness and allergy when applied to certain types of wounds. Meanwhile, MEDIACE® has demonstrated a positive response in animal models with diabetes and has no side effects so far, paving a way to enter human trials on patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Furthermore, AMS BioteQ’s dressing exhibits anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects on wounds. With a profile of high hydrophilicity and anti-adhesion, the dressing is fitted to use on wounds with all types of wound fluid.
Compared to using polyurethane or lyophilic colloids as the material, the dressing integrates gelatin which contains amino acids, which accelerates wound healing.
Capturing the Boom in Pet Economy
As the pet economy grows with an exponential speed, dressings for animals become a lucrative battlefield. Currently, MEDIACE® has entered animal studies. It has been examined on animal models with Chlamydia, Aeromonas, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas, and E. coli. The result showed the dressing has an antimicrobial effect on those bacteria.
Now, the dressing is aimed at the human market, targeting decubitus ulcers, foot ulcers, infectious wounds, or hard-to-heal wounds caused by cancer.
©www.geneonline.com All rights reserved. Collaborate with us: service@geneonlineasia.com








