Taiwan Breakthrough: Next-Generation Sequencing Now Covered in Health Insurance, Benefitting 20,000 Cancer Patients Annually
[Taipei, Taiwan; May 1, 2024] – Taiwan took a significant leap in healthcare advancements as the nation’s National Health Insurance (NHI) officially integrated next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing into its coverage benefits. This groundbreaking move aims to address a spectrum of cancers, ranging from non-small cell lung cancer to triple-negative breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and various solid and hematological tumors.
NGS, also referred to as second-generation sequencing or high-throughput sequencing, represents a cutting-edge technology evolved from first-generation sequencing methods. It boasts high-throughput capabilities, enabling swift detection of a multitude of genetic mutations. Targeted therapies and immunotherapies, newly emerged for cancer treatment, often require the identification of genetic mutations via biomarker testing to precisely pinpoint treatment targets. This novel technology equips clinicians with the tools to promptly identify suitable cancer-targeting drugs and offer patients tailored, precise treatment strategies.
Rare Testing Opportunity Yields Lasting Benefits
The National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA) will include coverage for NGS testing upon cancer diagnosis or when second-line or third-line therapies were unsuccessful. Under this plan, the NHI would cover one NGS test per cancer type for each insured individual, except in cases of cancer metastasis. Additional NHI-covered NGS tests are only available if the insured individual is diagnosed with a different type of cancer.
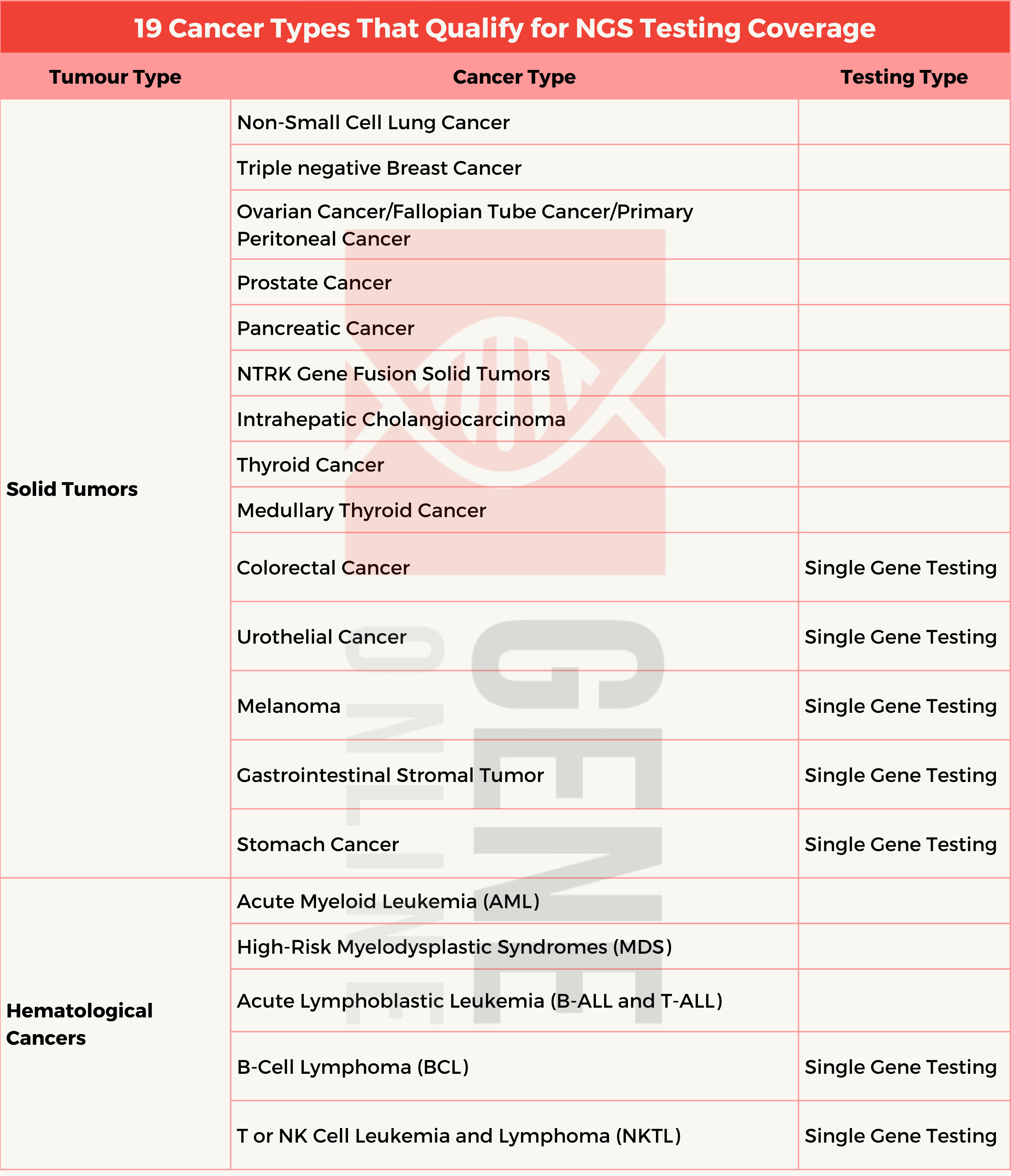
This system encompasses single gene testing, endorsed by experts, as well as more extensive multi-gene panel testing for 19 specific types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, ovarian cancer/fallopian tube cancer/primary peritoneal carcinoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, prostate cancer, melanoma, gastrointestinal stromal cancer, urothelial carcinoma, thyroid cancer/medullary thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, solid tumors with NTRK fusions, and pancreatic cancer. These advancements aim to ensure broader access to precision medicine for cancer patients.
NHIA Director General Chung-Liang Shih analyzed NHI data from 2022, revealing that a total of 830,000 patients had sought medical attention for cancer that year. Of the 39.2 billion NHI points spent on medications, the majority had been allocated to targeted therapies, accounting for approximately 61.7% of all expenses.
Reimbursement Options: Three Payment Tiers for NGS Test Coverage
Director General Shih has outlined a comprehensive approach to payment methods for NGS test coverage under the NHI. The NHI will reimburse 10, 20, and 30 thousand points, respectively, leaving the patient responsible for the remaining balance (with 1 NHI point equating to 1 NTD).

Under this scheme, individuals can choose between three distinct payment methods. Firstly, there’s the option for independent payment, particularly suitable for lengthy genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2. Secondly, payment is designated for a limited set of genes, usually fewer than 100, essential for each specific cancer type. Lastly, individuals can opt for payment covering a comprehensive set of genes, numbering over 100, providing a more detailed analysis.
These strategic initiatives have catapulted Taiwan to the forefront of global cancer treatment and precision medicine endeavors. The nation’s proactive approach not only expedites drug development and clinical implementation but also broadens treatment alternatives, promising enhanced quality of life for patients.
©www.geneonline.com All rights reserved. Collaborate with us: service@geneonlineasia.com










